If you have ever experienced the sharp pain and swelling associated with gout, you are not alone. Gout affects millions of people worldwide and can significantly impact their quality of life. In this article, we will explore the connection between high uric acid and gout, the symptoms of gout, and ways to manage and prevent it.
What is High Uric Acid?
Uric acid is a byproduct of purine metabolism, which is a natural process that occurs in the body. Purines are found in many foods, including red meat, seafood, and alcohol. However, when the body produces too much uric acid or is unable to eliminate it properly, it can accumulate in the body and lead to a condition called hyperuricemia.
Hyperuricemia is characterized by high levels of uric acid in the blood, and it is a common precursor to gout. While not everyone with hyperuricemia will develop gout, having high uric acid levels does increase the risk.
What is Gout?
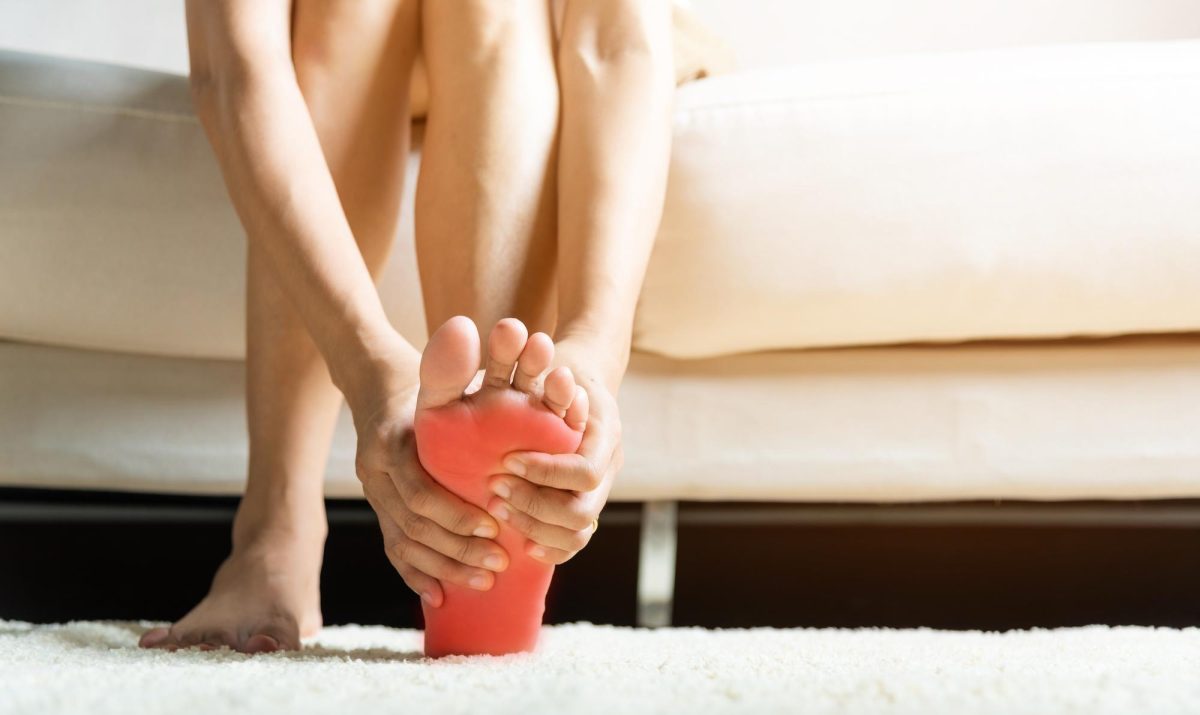
Gout is a form of arthritis that occurs when uric acid crystals accumulate in the joints, causing inflammation, pain, and swelling. The most commonly affected joint is the big toe, but gout can also occur in other joints, such as the ankle, knee, or elbow. The symptoms of gout usually come on suddenly and can be quite severe.
Gout has been around for centuries, and it has long been associated with excessive consumption of rich foods and alcohol. However, many factors can contribute to the development of gout, including genetics, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and kidney disease.

Symptoms of Gout
The symptoms of gout usually occur suddenly and can be quite severe. They often include:
Intense joint pain: The affected joint may be red, swollen, and extremely painful. Even the slightest touch can cause intense discomfort.
Warmth and redness: The affected joint may feel warm to the touch and appear red or purplish.
Limited mobility: The joint may become stiff and difficult to move.
Fever: Some people with gout may experience a low-grade fever.
Managing High Uric Acid and Gout
While there is no cure for gout, many ways exist to manage and prevent it. Here are some tips:
Medications: There are several medications available to treat gout, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids. Your doctor can help determine which medication is best for you.
Lifestyle changes: Changing your diet and lifestyle can help manage and prevent gout. This includes reducing the consumption of purine-rich foods, such as red meat, seafood, and alcohol, and staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can also help reduce the risk of gout.
If you experience symptoms of gout, it is important to see your healthcare provider. They can help diagnose and treat the condition, and offer advice on lifestyle changes to manage and prevent it.




















Share this article